What are some negative effects of musicon the brain.

Does music affect your mood? barry goldstein, a recording artist who has studied the vibrational effects of music for more than 25 years, says music has a profound impact on the brain. In recent years the effects music has on the human brain have been slowly demystified by leading neurologists. music's place in modern medicine has been around, in america, since the 1940s; the field is technically known as music therapy.
The playing and listening to music have positive effects on the brain. it makes one happier and productive at all stages of life and could delay the aging of the brain. listening to music after stroke not only promotes behavioral recovery but also induces fine-grained neuro-anatomical changes in brain recovery. There is no absolute piece of research which tells exactly how does music affect the brain, what type of music will help people perform better, so how you do ultimately depends on you. however, listening to music has shown that music affects the brain causing the release of dopamine, meaning a more rewarding and pleasurable experience which can. Whether you play an instrument, listen to your music streaming app, or enjoy going to live concerts, music is having an active influence on your brain. understanding how music and the mind interact, and how to fine-tune your music consumption for maximum impact, can have an effect on the way you feel, think, study and more.
How Listening To Music Benefits Yourbrain The Best
The mozart effect could be completely non-existent, according to a new neuro-scientific study in america. in a new study by nicholas spitzer at the university of california, it has been suggested that listening to classical music has no effect on the brain's capacity to learn and be active. this goes against the popular ensimismamiento of 'the mozart effect', which suggests that listening to classical music (and mozart in autónomo) can increase brain activity of developing babies and adults alike. That's one of the things jonathan burdette, m. d. has found in researching music's effects on the brain. "music is primal. it affects all of us, but in very unilateral, unique ways," said burdette. Music has been scientifically proven to have a powerful effect on the brain. recent research shows that music can help in many aspects of the brain, including pain reduction, stress relief, memory, and brain injuries. in the book the power of music, elena mannes says, “scientists have found that music stimulates more parts of the brain than any other human function. ” let’s look at some of the ways music can aid in the healing and stimulation of the human brain.
'the power of music' to affect the brain science all but confirms that humans are hard-wired to respond to music. studies also suggest that someday music may even help patients heal from parkinson. The harmful effects of music on body and mind are due to various factors. the most important of these is the kind or quality of the music. but there are others of a secondary character which can be influential and at times even decisive. there is also another psychological reason why accompanying music has a special effect upon the. This is enough time for music to have an effect on the brains of non-musicians as well. how music improves your mood and reduces stress. science has now proven what music lovers already fuera de combate, that listening to upbeat music can improve your mood. listening to and playing music reduces chronic stress by lowering the stress hormone cortisol. (10, 11).
The Harmful Effects Of Music On Body And Mind The

First the listening: the most obvious effect is stress reduction. stress, as i have explained in early posts, is the arch-enemy of memory ability. in my case, i put my west coast jazz experience. The mozart effect could be completely non-existent, according to a new neuro-scientific study in america. in a new study by nicholas spitzer at the university of california, it has been suggested that listening to classical music has no effect on the brain's capacity to learn and be active.
The relationship between man and music is a complex one. the ancient greco-roman culture believed music penetrated both the body and mind, bringing them into equilibrium. in contrast, europeans of the late 18 th century romantic era perceived music as a double-edged sword, capable of both curing and causing disorders (rose & bartsch, 2009). it is possible that these societies believed music. Research on the effects of music during exercise has been done for years. in 1911, an american researcher, leonard ayres, found that cyclists pedaled faster while listening brain music effect on has no the to music than they did in silence. this happens because listening to music can drown out our brain’s cries of fatigue.
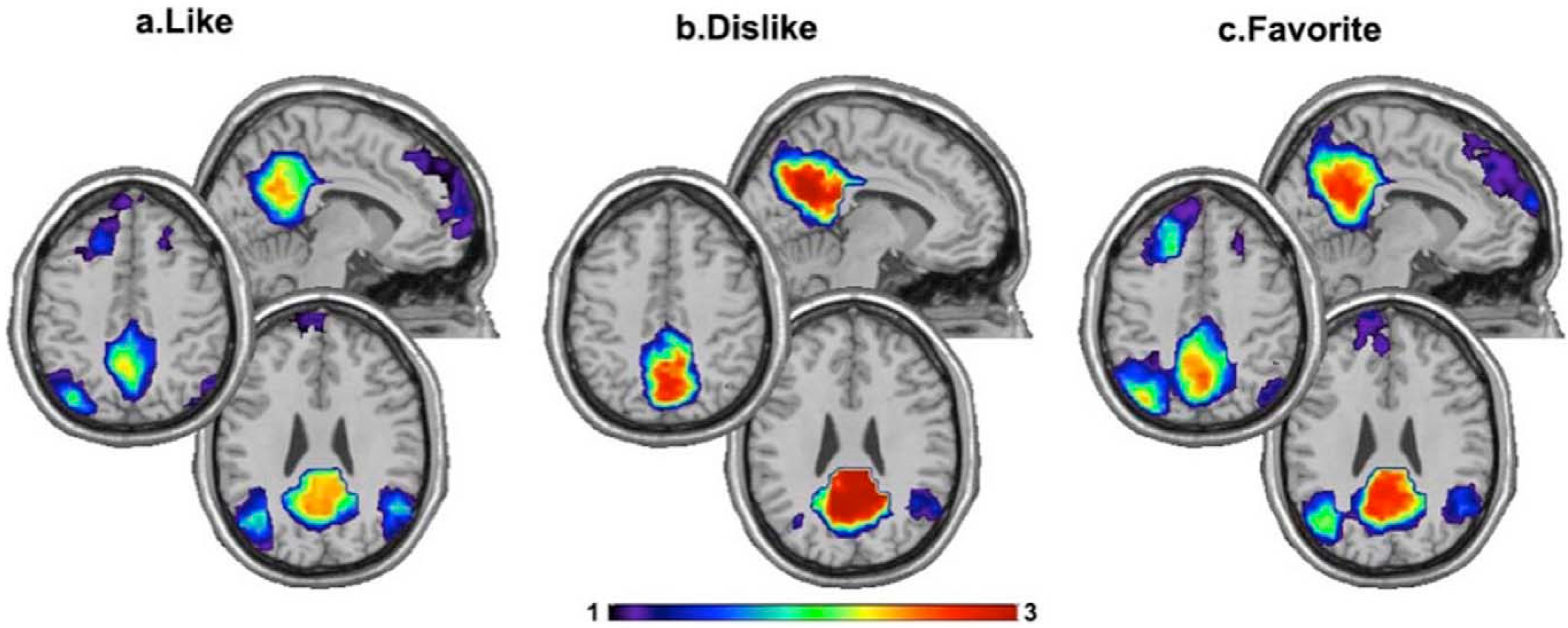
Not all types of music have favourable effects, however. too loud or too jarring music can be distracting, and can compete for our attention with what we're trying to do. but for the most part, exposure to music, specifically classics, has beneficial effects: 1 music heals. pain relief. overall, music does have positive effects on pain management. Musichas a profound effect on the brain. it connects the two hemispheres of the brain and activates many different parts of the brain, such as the motor cortex, sensory cortex, auditory cortex, hippocampus, cerebellum, amygdala, nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex. Musichas been scientifically proven to have a powerful effect on the brain. recent research shows that music can help in many aspects of the brain, including pain reduction, stress relief, memory, and brain injuries. in the book the power of music, elena mannes says, “scientists have found that music stimulates more parts of the brain than. Exposure to hard rock / acid rock music, regardless of gender, has been shown to inhibit the ability of some people’s brains to store the studied information correctly in the brain. rock music was found to increase adrenalin levels in a group of students, while a slow piano instrumental had a calming effect.
In this episode of tech effects, we explore the impact of music on the brain and body. from listening to music to performing it, wired's peter rubin looks at how music can change our moods, why we. Exactly what chemical processes occur when we put our headphones? scientists have come across some clues. It has the power of healing certain ailments. indian classical music has been found to have the strongest healing powers. music has a calming effect on the mind. it is known to speed the recovery of health ailments. it helps fight anxiety and has a soothing effect on the brain. effects of music on the mental state fights depression.
Research has concluded that music does have positive effects on our mind. it has the power of healing certain ailments. indian classical music has been found to have the strongest healing powers. music has a calming effect on the mind. That's one of the things jonathan burdette, m. d. has found in researching music's effects on the brain. "music is primal. it affects all of us, but in very independiente, unique ways," said burdette. Research shows that listening to music can reduce anxiety, depression, blood pressure, and pain as well as improve sleep quality, mood, memory, increase some cognitive functions, enhance learning and concentration, and ward off brain music effect on has no the the effects of brain aging. music is so good for your brain because it is one of the few activities that stimulates.
Music is a common phenomenon that crosses all borders of nationality, race, and culture. a tool for arousing emotions and feelings, music is far more powerful than language. an increased interest in. In recent years the effects music has on the human brain have been slowly demystified by leading neurologists. music's place in modern medicine has been around, in america, since the 1940s; the field is technically known as music therapy. music therapy is a multi-faceted branch of psychology,. In 60% of people who brain music effect on has no the have a stroke, the lente areas of the brain are affected. this leads to ‘visor neglect’: the patient loses awareness of objects on the opposite side to where the brain has been damaged. but, studies have found, when patients listen to their favourite music, some of their lente attention is restored (tsai et al. 2013).
Beneficial effects of music on health & brain.
Komentar
Posting Komentar